Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria For Alzheimer's Disease
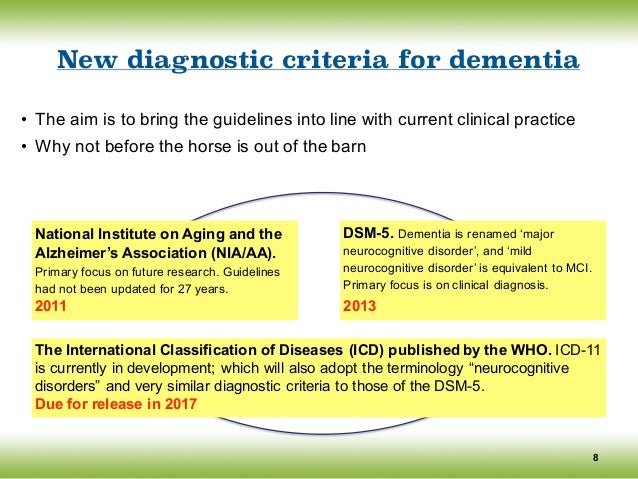
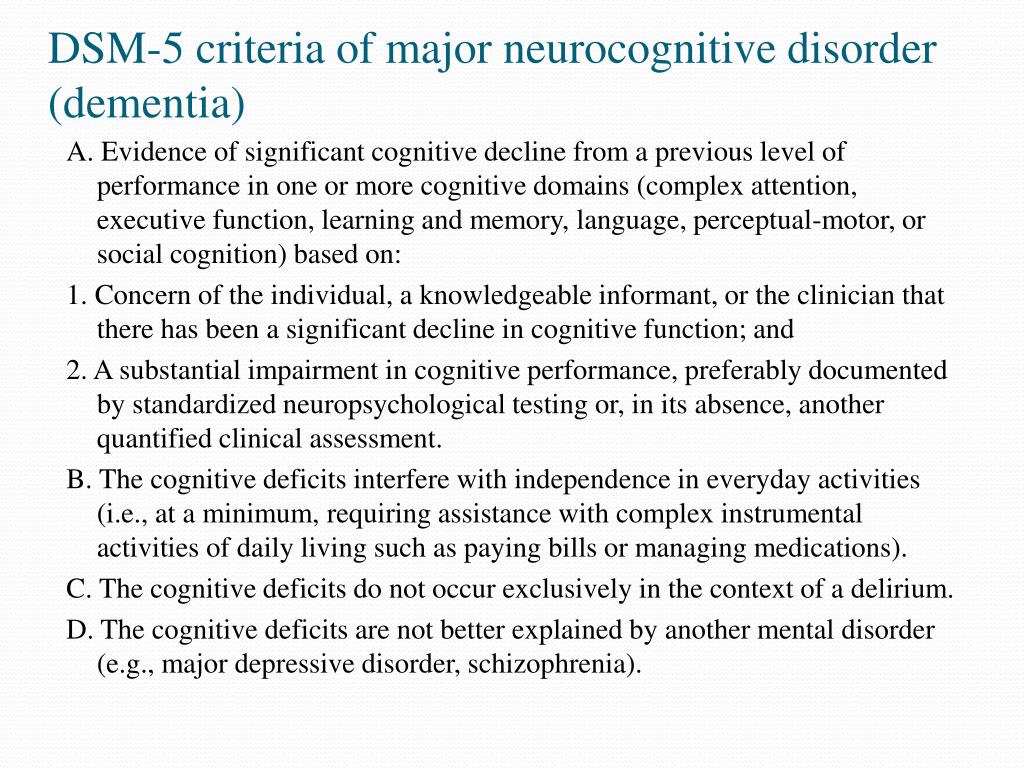
Dsm 5 diagnostic criteria for alzheimer's disease. The existing criteria in DSM IV subsume PD-D under dementia due to other medical conditions and the section specifically devoted to PD-D is rather descriptive. In order to meet the DSM5 criteria for AD the individual must meet the criteria for major or mild neurocognitive disorder and there should be insidious onset and gradual progression of. The New Requirements for Alzheimers Diagnosis.
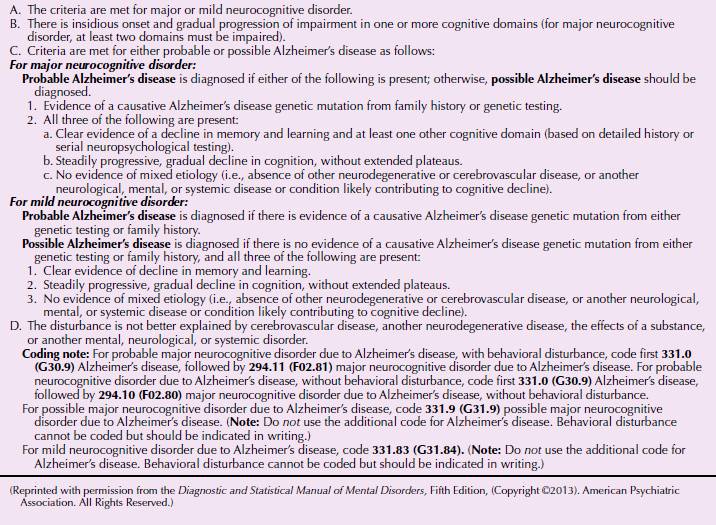
Probable or possible Alzheimers disease dementia with evidence of the Alzheimers disease pathological process. AD diagnostic criteria NIA-AAIWG guidelines. There are no specific and operationalized criteria to diag-nose dementia associated with PD PD-D.
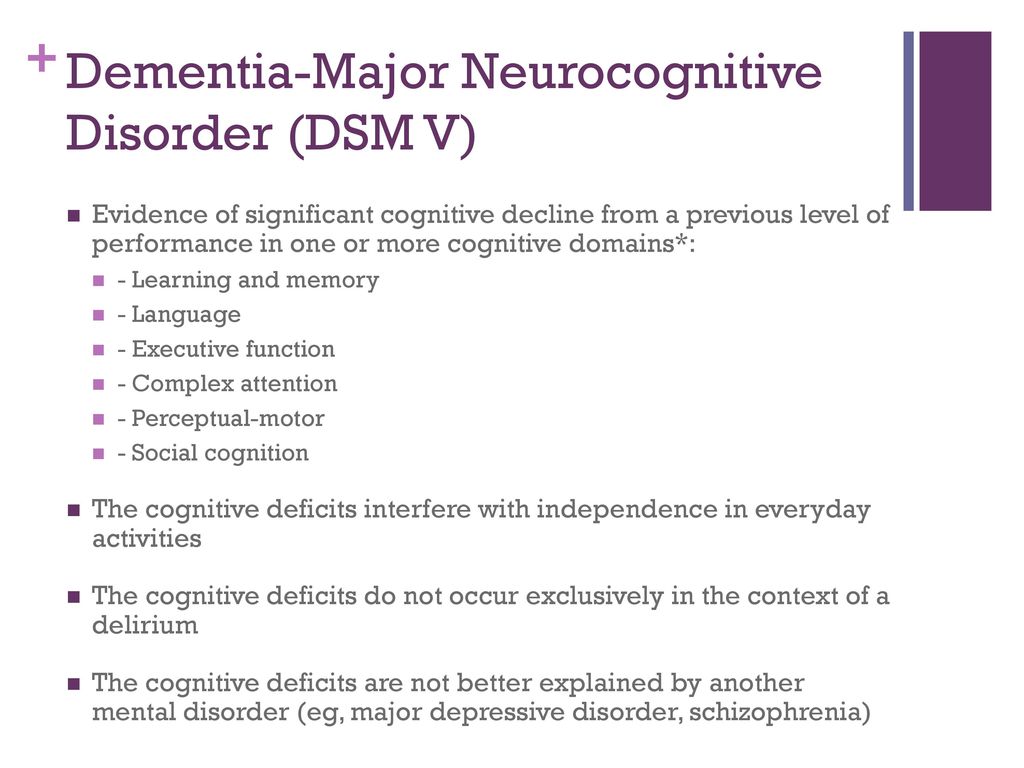
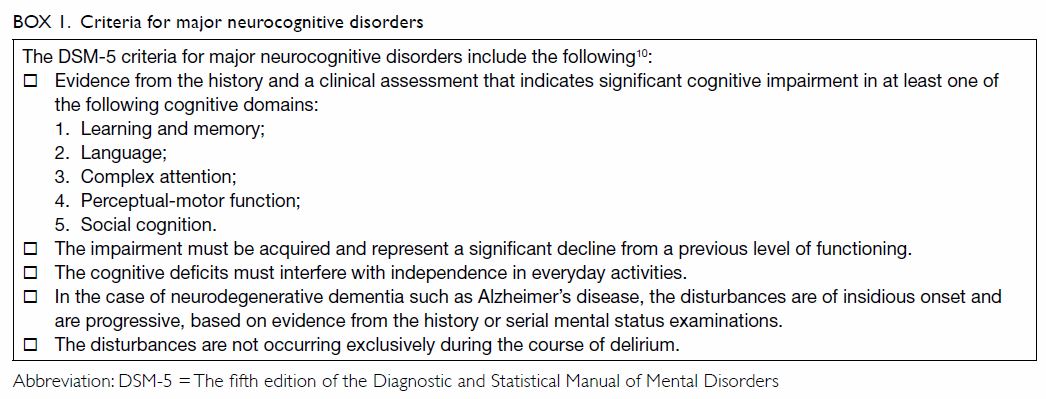
Alzheimers Disease Subtype of Major or Minor Neurocognitive Disorders DSM-5 A. Insidious onset with gradual decline in one or more cognitive abilities for major neurocognitive disorder at least two domains must be impaired. Etiology Specify whether due to.
The DSM -V diagnostic criteria for major or mild neurocognitive disorder due to Alzheimers disease includes the following. Preclinical prodromalMCI mild moderate severe AD. Or c evidence for another neurological disease or a non-neurological medical comorbidity or medication used that could have a substantial effect on cognition.
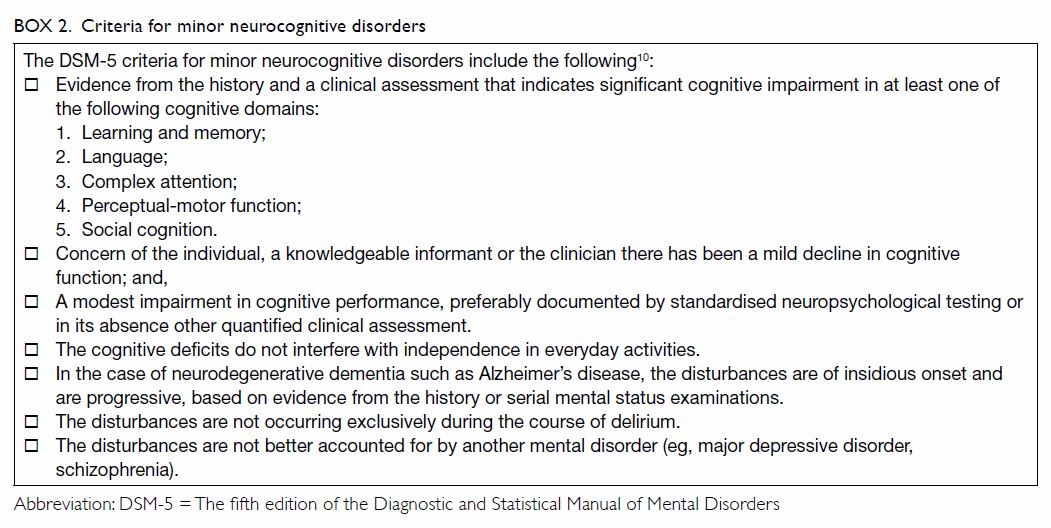
An early and significant episodic memory impairment. DSM-5 For more information see Major and Mild Neurocognitive Disorders. Despite differing target audiences and scope it is possible to compare the Fifth Edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM-5 American Psychiatric Association.
As potential ther-apeutic approaches for PD-D become available and clin-ical trials are underway it is important to establish spe-. Meets criteria for Major Neurocognitive Disorder with memory being one of the impaired domains. Disease continuum.
Memory impairment Aphasia Apraxia Agnosia Executive dysfunction. Clinicobiological entity ICD 10 DSM 5 major and mild neurocognitive disorder Consensus for research purposes and trial enrichment.
Memory impairment Aphasia Apraxia Agnosia Executive dysfunction.
Or b features of dementia with Lewy bodies other than dementia itself. The existing criteria in DSM IV subsume PD-D under dementia due to other medical conditions and the section specifically devoted to PD-D is rather descriptive. Core clinical diagnosis biomarkers. Evaluation of DSM-5 and IWG-2 criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimers disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Insidious onset with gradual decline in one or more cognitive abilities for major neurocognitive disorder at least two domains must be impaired. As potential ther-apeutic approaches for PD-D become available and clin-ical trials are underway it is important to establish spe-. DSM-5 For more information see Major and Mild Neurocognitive Disorders. Disease continuum. Alzheimers Disease Subtype of Major or Minor Neurocognitive Disorders DSM-5 A.
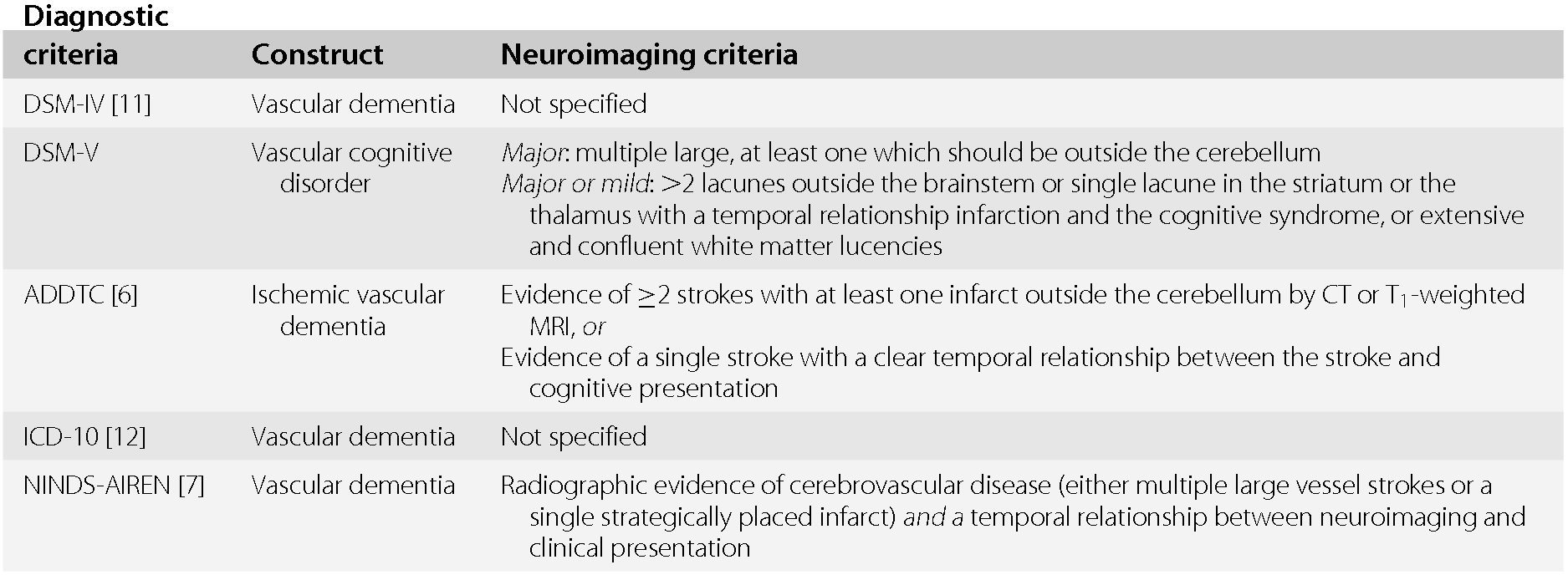
Memory impairment Aphasia Apraxia Agnosia Executive dysfunction. Some individuals with Parkinsons disease and dementia are found at autopsy to have coexisting neuropathology indicative of Alzheimers disease or of diffuse Lewy Body disease. Meets the core criteria for AD dementia but has evidence of a concomitant cerebrovascular disease. Core clinical diagnosis biomarkers. Probable or possible Alzheimers disease dementia with evidence of the Alzheimers disease pathological process. Alzheimers Disease Subtype of Major or Minor Neurocognitive Disorders DSM-5 A. DSM-5 For more information see Major and Mild Neurocognitive Disorders.































Post a Comment for "Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria For Alzheimer's Disease"