Antidepressants And Liver Disease
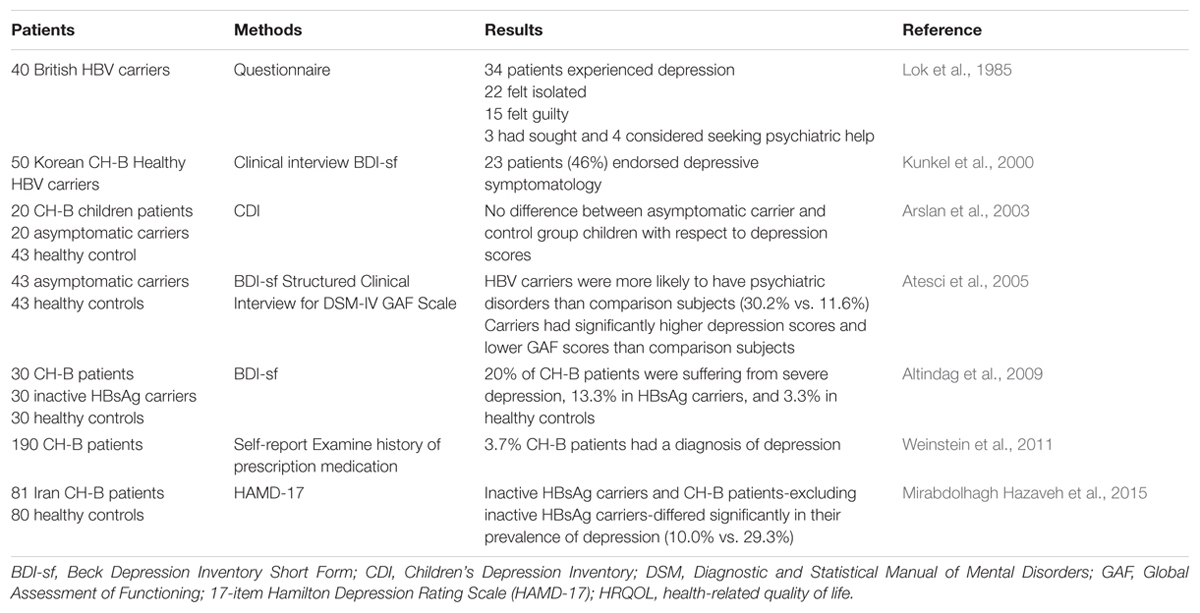
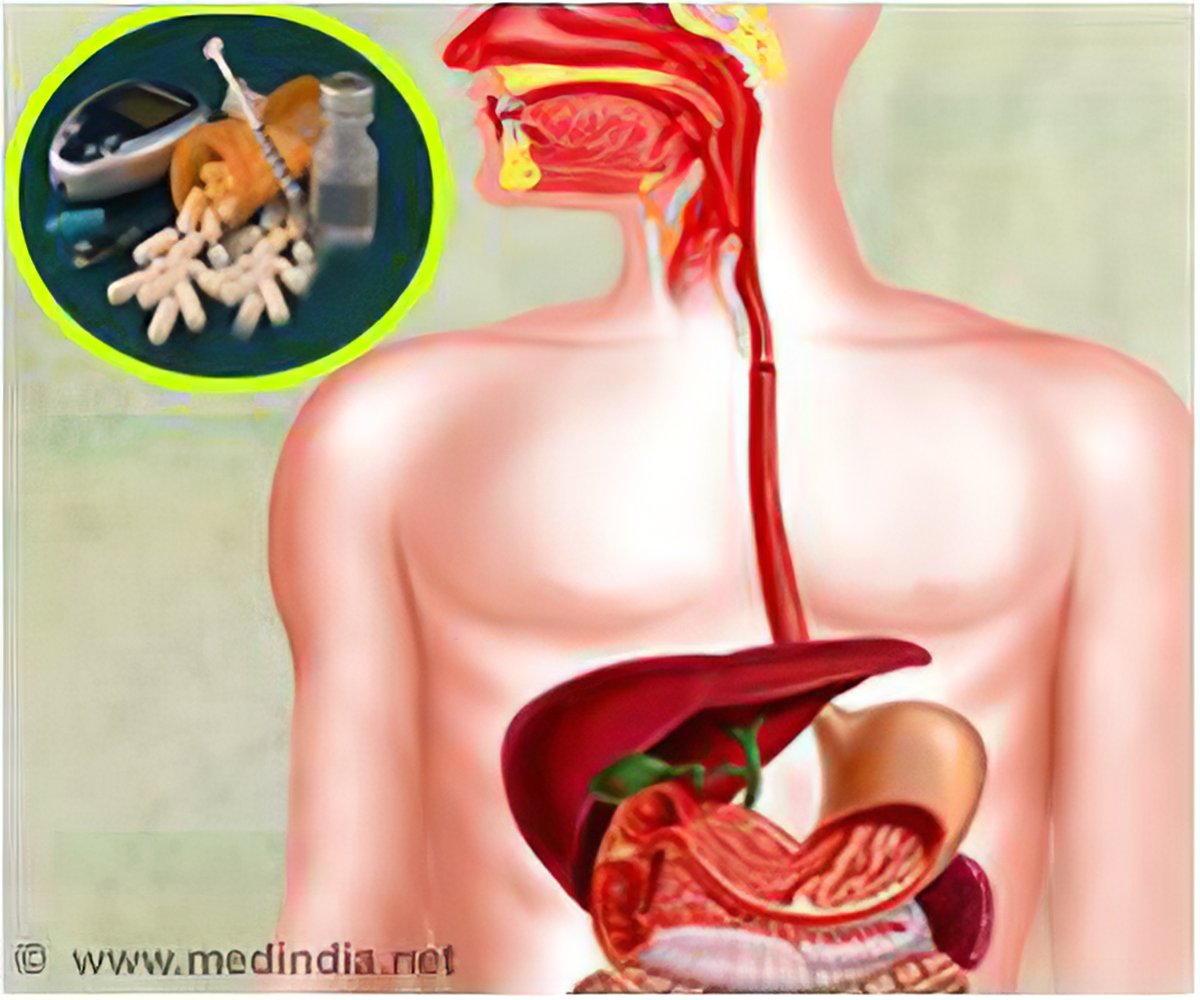
Antidepressants and liver disease. Patients with cirrhosis were found to be extremely sensitive to tranylcypromine and the use of this drug for the treatment of depression in such patients is contraindicated. Amitriptyline has a wider margin of safety in such patients but caution is necessary when the. Only a few cases of hepatic injury involve patients with chronic hepatitis infection.
INTERACTION BETWEEN CHEESE AND MONOAMINE-OXIDASE INHIBITORS IN RATS AND CATS. Spective analysis of patients with end-stage liver disease of different aetiologies who received OLT demonstrated that amongst patients with depression prior to surgery those taking antidepressants at the time of OLT experi-enced significantly less acute cellular rejection 13 than depressed patients not receiving antidepressants. Depression and the use of antidepressants in patients with chronic liver disease or liver transplantation Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
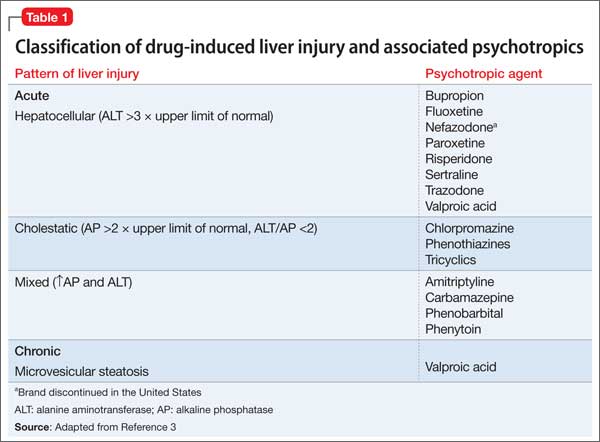
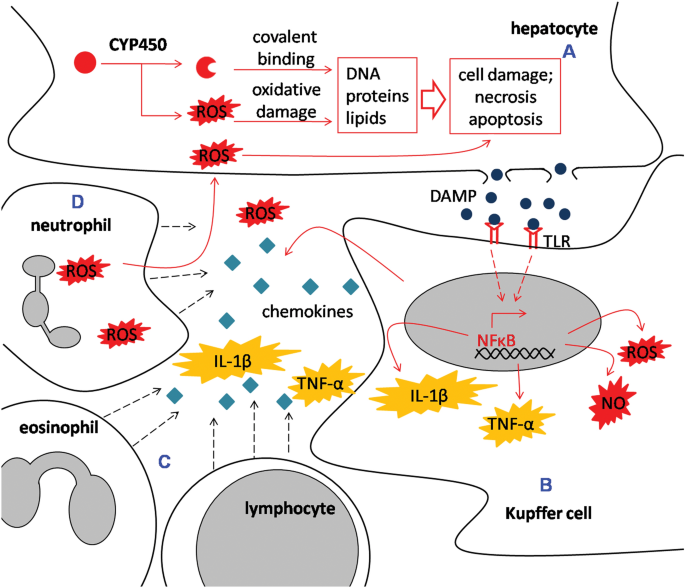
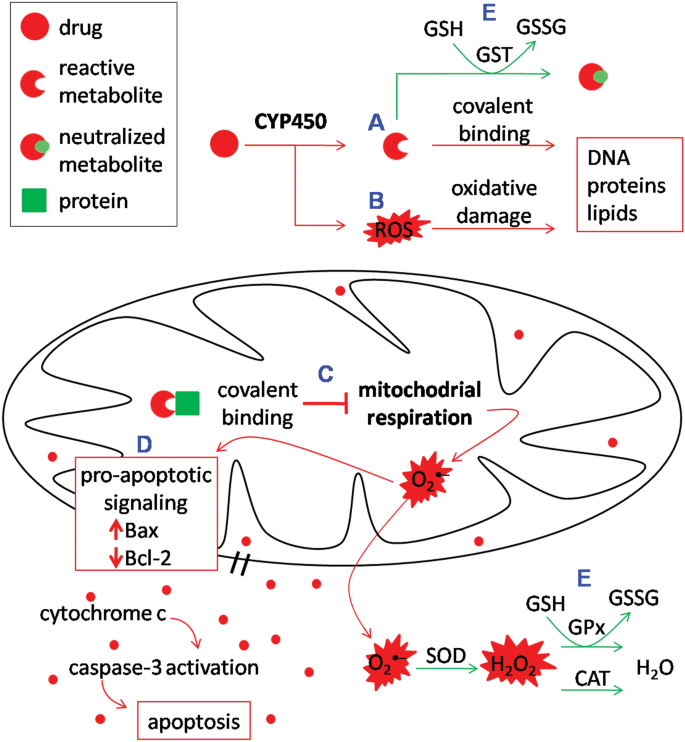
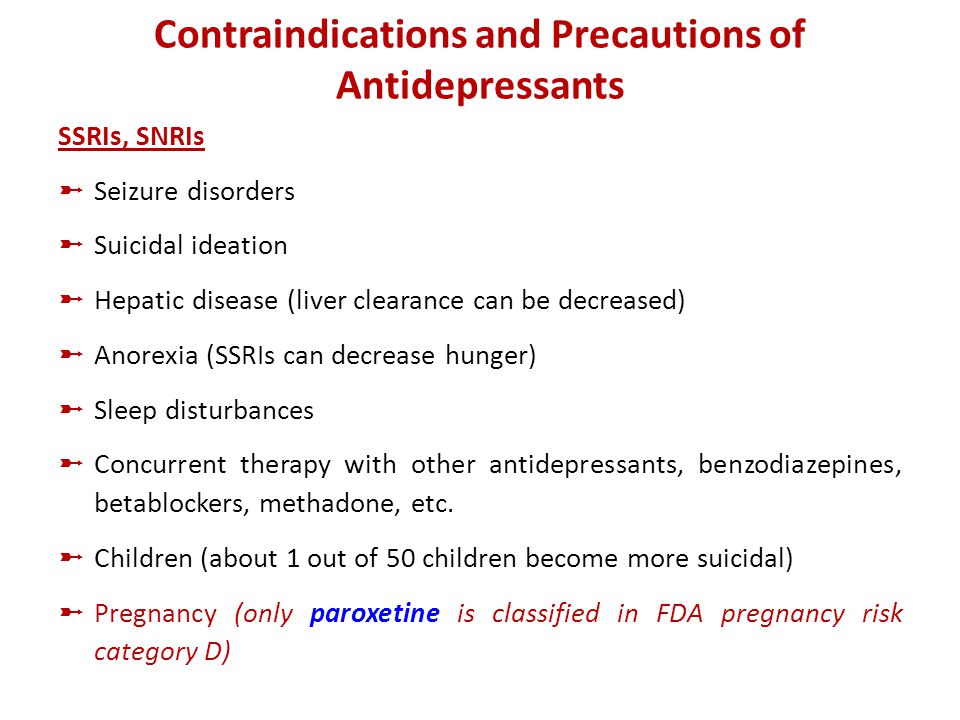
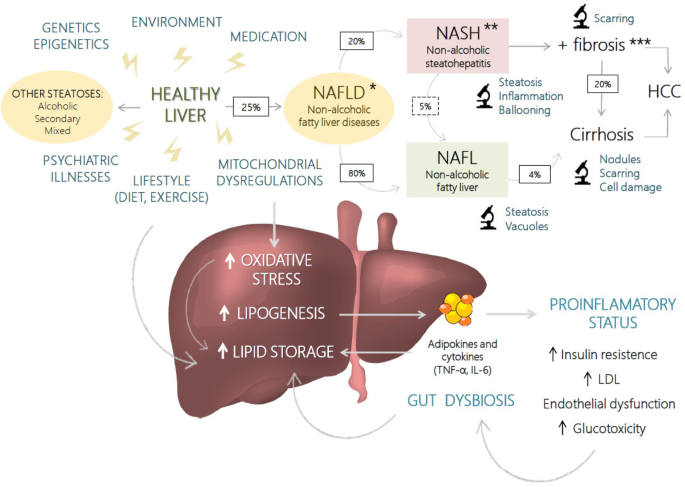
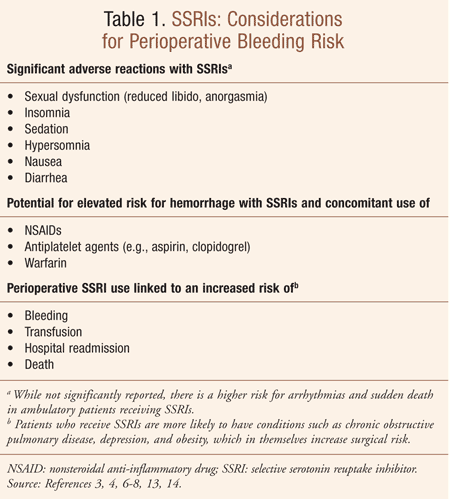
Drugs whose risks are apparently lower include citalopram escitalopram paroxetine and fluvoxamine. Antidepressant-induced liver injury includes various biologicalandclinicalpresentationsrangingfromisolated increases in liver enzyme levels to nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue asthenia anorexia nausea vomiting and upper right abdominal pain and also to more specific symptoms such as jaundice dark urine or pale stool progressive or even fulminant liver failure. Antidepressant-induced liver injury can occur in the absence of identifiable underlying risk factors such as cirrhosis and hepatitis infection.
Increased vasodilating substances such as nitric oxide activate the renin angiotensin aldosterone system leading to vasoconstriction. Although data on antidepressant-induced liver injury are scarce 05-3 of patients treated with antidepressants may develop asymptomatic mild elevation of serum aminotransferase levels. Amines in blood and urine in relation to liver disease.
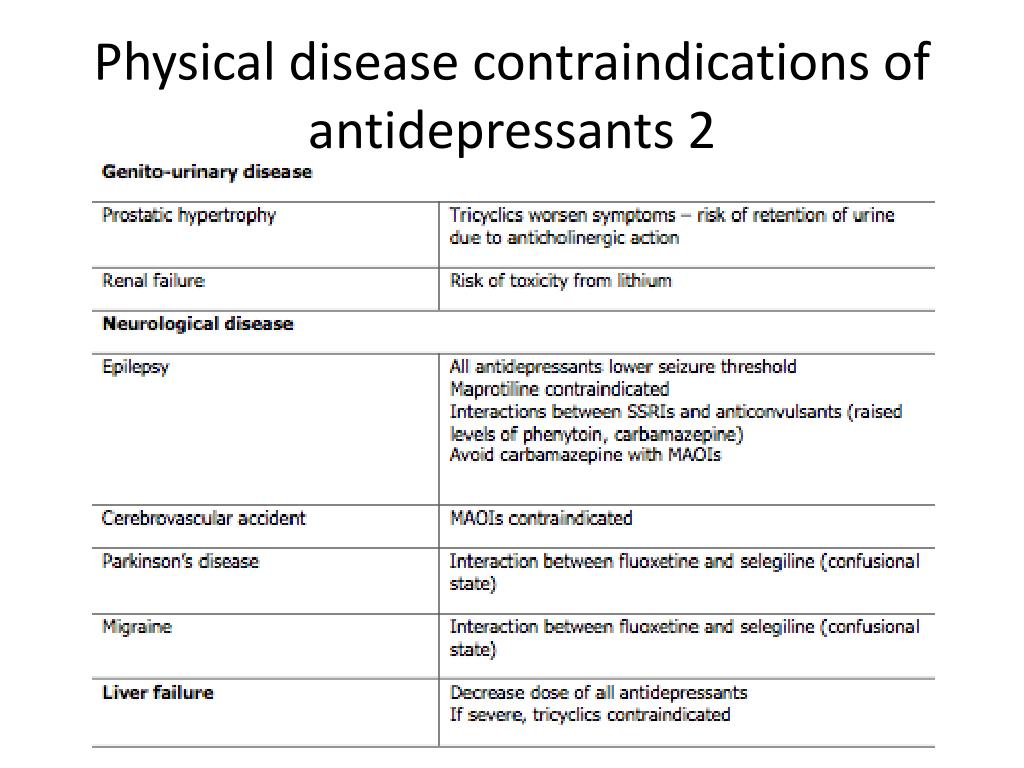
Selecting Appropriate Antidepressant Tx for Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Liver Transplantation The scale of depression in patients with chronic liver disease. The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs should also be avoided particularly in moderate-severe liver disease. Patients with cirrhosis were found to be extremely sensitive to tranylcypromine and the use of this drug for the treatment of depression in such patients is contraindicated.
12 linhas A retrospective analysis of patients with end-stage liver disease of different aetiologies who. READ Fromthe DepartmentofMedicine University ofBristol at BristolRoyalInfirmary SUMMARY Patients with cirrhosis were found to be extremely sensitive to tranylcypromine and theuseofthis drugforthetreatmentofdepressioninsuchpatientsis contraindicated. All antidepressants can induce hepatotoxicity especially in.
Antidepressants andliver disease M. Onset of antidepressant-associated hepatotoxicity varies from 5 days to 3 years.
Antidepressants and liver disease.
Antidepressants and liver disease. All antidepressants can induce hepatotoxicity especially in elderly patients and those taking more than one drug Liver damage is generally unpredictable and unrelated to dose Liver damage can occur within a few days of initiation Antidepressant-induced liver failure can be life threatening. If liver disease is present it is preferable to use psychotropic drugs with minimal liver metabolism eg topiramate sulpiride and amisulpride. Although data on antidepressant-induced liver injury are scarce 05-3 of patients treated with antidepressants may develop asymptomatic mild elevation of serum aminotransferase levels. Amitriptyline has a wider margin of safety in such patients but caution is necessary when the. Antidepressants and liver disease. 12 linhas A retrospective analysis of patients with end-stage liver disease of different aetiologies who. Patients with cirrhosis were found to be extremely sensitive to tranylcypromine and the use of this drug for the treatment of depression in such patients is contraindicated. Selecting Appropriate Antidepressant Tx for Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Liver Transplantation The scale of depression in patients with chronic liver disease.
READ Fromthe DepartmentofMedicine University ofBristol at BristolRoyalInfirmary SUMMARY Patients with cirrhosis were found to be extremely sensitive to tranylcypromine and theuseofthis drugforthetreatmentofdepressioninsuchpatientsis contraindicated. Depression and the use of antidepressants in patients with chronic liver disease or liver transplantation Aliment Pharmacol Ther. Antidepressant-induced liver injury includes various biologicalandclinicalpresentationsrangingfromisolated increases in liver enzyme levels to nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue asthenia anorexia nausea vomiting and upper right abdominal pain and also to more specific symptoms such as jaundice dark urine or pale stool progressive or even fulminant liver failure. In cirrhosis patients have a hyperdynamic circulation. BLACKWELL B MARLEY E. Dallos V Heathfield K. Antidepressant-induced liver injury can occur in the absence of identifiable underlying risk factors such as cirrhosis and hepatitis infection.




























Post a Comment for "Antidepressants And Liver Disease"